Stone
It is always obtained from rock, which is solid portion of earth crust. It is small piece of rock.
• Stone may be in the form of Stone block & Stone slab.
e.g.- basalt, granite, marble, Kota etc.
 |
| Various types of stone |
Characteristics of good building stone.
A good building stone should have the following qualities:
- Appearance: The Appearance of stone should be good whenever used for face work of a building. Stone should be hard enough so that due to atmospheric action it should not be change. Stone should able to receive good polish. Light coloured stone are generally preferred.
- Strength: Strength of stone should be high so that they can withstand against various loads on them and disintegrated actions of weather. Stone should be tested for their strength before they are used for loaded and heavy structure.
- Structure: A broken stone should have uniform and dense texture. It Should be free from cavities, cracks and patches.
- Durability: Durability of stone depends upon its chemical composition and physical structure. Stone should possess a natural durability to withstand the destructive effects of various agents which are continuously operating on them so a good stone should have compact and crystalline structure.
- Hardness: The Stone should be hard enough to resist the abrasive forces and frictional forces.
- Toughness: Good stones should be tough enough to withstand stresses developed due to vibrations of machinery and moving loads over them.
- Specific gravity and weight: For good quality of building stones specific gravity should be high. It should be lie between 2.4 to 2.8 . For construction of massive structures such as dams,barrages, retaining walls heavier stones are preferred where as for arches, roof covering, domes etc. light weight stones may be the choice.
- Workability: Stone should be such that its cutting dressing, shaping is not so hard otherwise to work with it becomes uneconomical i.e. stone should be workable.
- Fire Resistance: Stone should be such that it is able to resist high temperature whenever it comes in contact with fire and heat.
- Cost: The Cost of stone depends upon the ease with which it can be quarried out, the proximity of quarry to the place of use and the transportation facilities available. The cost of dressing a stone should also low.
Details of common building stone
Granite: It is geologically Igneous rock, physically unstratified rock and chemically silicious rock. It is composed of quartz, felspar and mica.
Characteristics:
Characteristics:
- Specific gravity lie between 2.63 to 2.75.
- It is hard, strong and durable.
- Crushing Strength-1000kg/cm^2 to 2500kg/cm^2.
- It developed crack badly under fire.
- Colour- grey, green, pink.
Uses:
- It is used for decorative purpose.
- Inferior quality used aggregate in concrete, ballast in railway track.
Occurrence:
- Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh etc.
Sandstone: It is geologically sedimentary rock, physically Stratified rock and chemically silicious rock. It is composed of sand, mica, felspar, magnetite and oxide of iron.
Characteristics:
- Specific gravity lie between 2.65 to 2.95.
- Colour- grey, yellow, light brown, and blue.
- It is soft and porous stones.
- Compressive strength- 65kg/cm^2.
- It is resistance to fire.
Uses:
- Road metal inferior quality of sandstone used.
- Good quality, for rubble masonry work.
Occurrence:
- Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan etc.
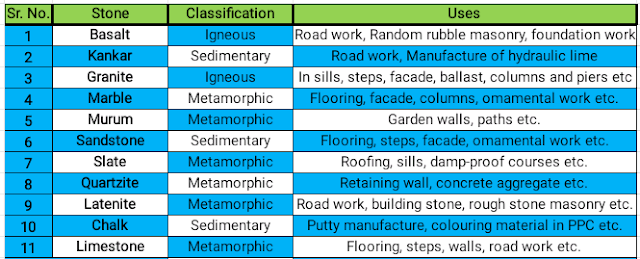 |
| Table No. 1 |
Basalt and Trap: It is geologically igneous rock, physically unstratified rock. It consist of felsper, alumina, silica and other material.
Characteristics:
Characteristics:
- Specific gravity lie between 2.6 to 3.0.
- It is hard, compact and durable.
- It is less porous.
- It has grey, black, blue colour.
- Difficult to work with these stone.
Uses:
- It is used as road metal and railway ballast.
- These stone are used for construction steps.
Occurrence:
- Bihar, Gujrat etc.
Slate: It is geologically metamorphic rock, physically stratified rock and chemically argillaceous rock.
Characteristics:
- Specific gravity lie between 2.7 to 2.9.
- Compressive strength-700kg/cm^2 to 2100kg/cm^2.
- Colour- purple
- It is hard and tough.
- It is available in a number of colour.
Uses:
- It is used in flooring,damp proofing.
- It is used roof covering.
Occurrence:
- Rajasthan etc.
Deterioration of stones
The principal agencies responsibility for causing deterioration of stones are given below:
- Rain: As the rain water is not pure and contains many chemicals, when this water falls on stones the chemicals present in rain water react with stone and finally result in its deterioration.
- Frost: In the damp climate the moisture penetrates and gets filled up the pores of the stone. When this water freezes during Frost there consequent increase in volume of this water. This cause rupture of outer layers of stone.
- Wind: If dust is present in air then it's causes deterioration of stone because of the abrasive effect of dust particles.
- Polluted Atmosphere: In the big industrial cities, atmosphere is general polluted with smokes. Limestone's, calcareous sandstone and other stones containing carbonate of lime are much affected by this agency.
- Temperature Variation: The changes in temperature leads to alternate and unequal expansion and contraction of the different minerals of the stone. This results in development of large stresses and strains inside the stone and finally deterioration of stone
- Vegetable Growth: Some times plants grow in the stone structure. The roots of these plants penetrate through in the joints of stone masonry and ultimately leads to deterioration of stone.
- Effect Of Dissmilar Stones: When limestone and sandstone are used together during construction, then there is a tendency for the sandstone to decay.


Very good sir
ReplyDeleteNice
ReplyDelete